Last updated on September 18th, 2025 at 02:05 pm
Desalination, also popularly known as desalting, is the process of removing salt from the ocean water to convert it into a fresh water source. The water which is desalinated can be used for various purposes like drinking, industrial, commercial and agricultural use.
In an era where freshwater scarcity is becoming an escalating global crisis, the desalination of seawater stands as one of the most viable solutions. At our core, we understand the complexity of transforming saline water into a sustainable freshwater source. The process of seawater desalination is a multi-stage, technically precise operation that ensures high-quality water suitable for domestic, agricultural, and industrial applications.
Why Seawater Desalination Matters in Today’s Environment
With nearly 97.5% of the Earth’s water stored in oceans and seas, and only a minuscule percentage available as freshwater, the conversion of saline water into usable forms is imperative. As population growth, industrial expansion, and climate change strain traditional water resources, seawater desalination offers a consistent, weather-independent water supply.
Step 1: Seawater Intake and Pre-Screening
The desalination journey begins with the intake of seawater, typically from coastal areas. Intake systems must be engineered to minimize environmental impact and reduce damage to marine ecosystems. Two primary methods are employed:
- Open Intakes: Large-volume pumps draw water directly from the ocean.
- Subsurface Intakes: Water is filtered naturally through beach sediments before reaching the system.
Once collected, pre-screening involves the removal of large debris, fish, and other particulates using bar screens and coarse filters. This protects downstream components from fouling and mechanical damage.
Step 2: Pre-Treatment – Preparing Seawater for Desalination
Before entering the core desalination unit, seawater undergoes pre-treatment to eliminate suspended solids, biological contaminants, and chemical pollutants. The efficiency of this stage is critical for long-term performance and membrane lifespan.
Key components of pre-treatment include:
- Coagulation and Flocculation: Chemicals like ferric chloride or aluminum sulfate cause suspended particles to aggregate.
- Media Filtration: Dual or multi-media filters trap fine particulates.
- Cartridge Filtration: Final polishing filters (usually 5-micron) to remove residual impurities.
- Chemical Dosing: Antiscalants, biocides, and pH adjusters are introduced to stabilize the water chemistry.
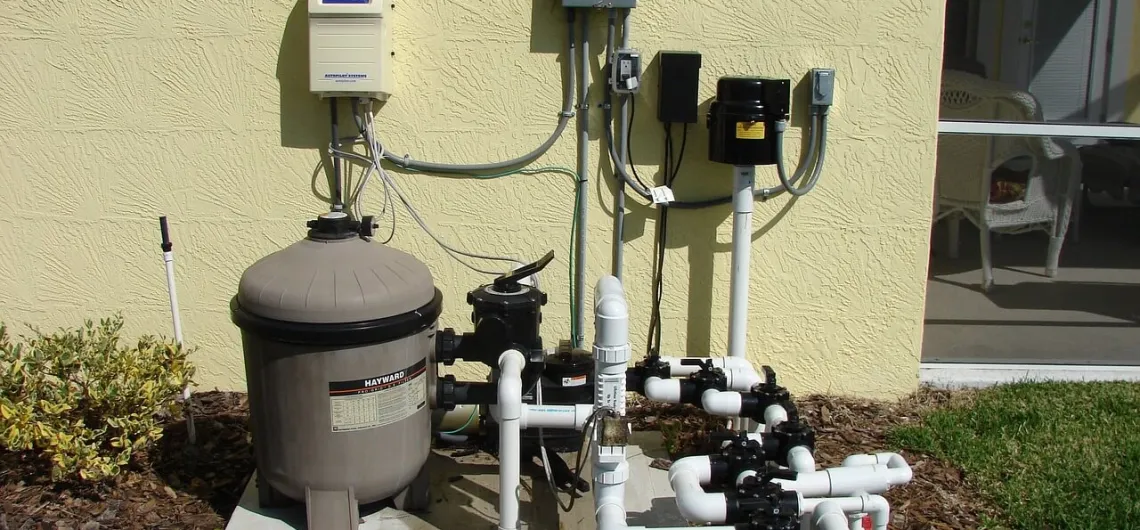
Step 3: Core Desalination via Reverse Osmosis (RO)
The most prevalent method in modern desalination facilities is Reverse Osmosis, a pressure-driven membrane process that separates dissolved salts and impurities from water molecules.
How Reverse Osmosis Works
- High-pressure pumps (800–1200 psi) force seawater through semi-permeable membranes.
- These membranes allow only water molecules to pass, retaining salts, pathogens, and organics.
- The output is twofold:
- Permeate (Product Water): Clean, desalinated water.
- Concentrate (Brine): Saline reject stream.
Advanced systems incorporate energy recovery devices (ERDs) like pressure exchangers, significantly reducing operational energy demands by recycling pressure from the brine.
Alternative Desalination Technologies
While RO dominates, other technologies serve niche or large-scale applications:
Multi-Stage Flash Distillation (MSF)
- Seawater is heated and flashed into vapor across successive chambers with decreasing pressure.
- Vapor condenses on heat exchanger tubes, yielding freshwater.
- Extremely durable and suited for large-scale municipal desalination.
Multi-Effect Distillation (MED)
- Operates on similar principles to MSF but with higher thermal efficiency.
- Each effect uses the vapor from the previous one for heating, minimizing energy usage.
Vapor Compression (VC)
- Utilizes mechanical or thermal compression of vapor.
- Typically applied in smaller, isolated installations where electricity is accessible.
Step 4: Post-Treatment – Water Conditioning
After desalination, the water is pure but may lack essential minerals and stable pH for safe distribution. Post-treatment reintroduces:
- Calcium and Magnesium for taste and corrosion control.
- Carbon Dioxide for pH stabilization.
- Chlorination or UV Sterilization for microbial safety.
- Fluoride (where required) for dental health compliance.
This stage ensures the water meets or exceeds WHO and EPA drinking water standards.
Step 5: Brine Management and Environmental Discharge
Brine, the highly saline concentrate from desalination, must be responsibly managed to prevent ecological disruption. Effective brine handling includes:
- Diffuser Systems: Blend brine with seawater at the discharge point to reduce salinity shock.
- Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): Advanced systems that recover almost all water and leave solid salt residue.
- Deep-Well Injection and Solar Evaporation Ponds in arid zones.
Strict adherence to local environmental regulations is essential for sustainable operations.
Energy Considerations and Cost Optimization
Desalination has historically been criticized for its high energy footprint. Modern facilities address this with:
- Energy Recovery Devices (up to 98% efficient).
- High-efficiency membranes and advanced pre-treatment.
- Hybrid Systems integrating solar, wind, and geothermal energy.
- Smart monitoring systems for predictive maintenance and optimized flows.
While costs vary, ongoing innovations are pushing the cost of desalinated water below $0.50 per cubic meter in many regions.
Materials and Equipment in Desalination Plants
To resist corrosion and biofouling in saline environments, materials used must be marine-grade and chemical-resistant:
- Duplex Stainless Steel and Titanium for high-pressure piping and membrane housings.
- HDPE and PVC for low-pressure lines and brine handling.
- Epoxy-lined tanks, ceramic membranes, and UV-resistant polymers for long-term durability.
Applications of Desalinated Water
Desalinated water is widely used across sectors, including:
- Municipal Supply: Drinking water for coastal cities and island nations.
- Industrial Processing: Boiler feedwater, electronics manufacturing, and textiles.
- Agriculture: Drip irrigation systems using blended desalinated water.
- Emergency Relief: Mobile desalination units in disaster zones and military bases.
Why can’t Desalination be used on a large-scale?
- Desalination is a highly efficient and effective method to convert salted water into pure and fresh drinking water but is also highly energy intensive. So, it becomes quite difficult to consider it on large-scale. For this reason, other options are considered before choosing desalination as a solution to the water crisis issue in a region. The agencies, governments, and authorities always consider drilling wells, installing treatment plants and using conservation methods before actually going for seawater desalination to provide the population with the fresh and pure water.
- Another reason for not opting desalination as a solution when it comes to providing water supply on a large-scale is money. There are things which make desalination process an expensive one. There are cases where water needs to be treated before the process of desalination takes place. This will require equipment, manpower, and facilities as well, which makes water expensive. Thus, aside from consuming a great deal of energy desalination is also a costly process.
Future of Sea Water Desalination
We are witnessing a new era where AI-driven process control, next-gen membranes, and off-grid solutions redefine the potential of seawater desalination. Emerging methods like membrane distillation, capacitive deionization, and forward osmosis promise even greater efficiency and lower carbon footprints.
As global water demand intensifies, the refined, scalable, and cost-effective process of seawater desalination remains a cornerstone in securing our planet’s freshwater future.
Seawater Desalination system FAQs:
- What is seawater desalination?
Seawater desalination is the process of removing dissolved salts and other impurities from seawater to produce fresh, drinkable water suitable for human consumption, agriculture, and industrial use.
- Why is seawater desalination important?
Desalination is vital in regions facing water scarcity, especially coastal areas with limited freshwater resources. It provides a reliable, sustainable supply of clean water for growing populations, industries, and agriculture.
- What are the main methods of seawater desalination?
The two most common methods are:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): Uses semi-permeable membranes and high pressure to filter out salts.
- Thermal Distillation: Heats seawater to produce vapor, which is condensed into freshwater.
- How does the reverse osmosis (RO) desalination process work?
In RO desalination, seawater is pretreated to remove large particles and microbes, then pumped under high pressure through special membranes that block salt molecules while allowing water molecules to pass through, producing freshwater.
- What is thermal desalination and how does it differ from RO?
Thermal desalination involves heating seawater until it evaporates and then condensing the vapor into freshwater. Unlike RO, which relies on membranes and pressure, thermal methods use heat energy, often from fossil fuels or renewable sources.
- Is desalinated water safe to drink?
Yes. Desalinated water is safe to drink once minerals are added back to balance its taste and nutritional value. The process ensures harmful salts, microorganisms, and contaminants are removed.
- What are the challenges of seawater desalination?
Some challenges include:
- High energy consumption
- Cost of construction and operation
- Disposal of concentrated brine (salt-rich wastewater)
- Environmental impacts on marine ecosystems
- What happens to the salt removed during desalination?
The removed salt and concentrated brine are usually discharged back into the sea. However, this must be carefully managed to prevent harm to marine life. Some industries also explore using the extracted salts for commercial purposes.
- Is desalination environmentally friendly?
Desalination provides clean water but raises environmental concerns such as greenhouse gas emissions from energy use and ecological effects from brine discharge. Using renewable energy and advanced brine management helps reduce these impacts.
- Which countries rely most on seawater desalination?
Countries in the Middle East (like Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Kuwait), as well as regions in Australia, Spain, and the U.S. (California, Texas), rely heavily on desalination to meet their freshwater needs.










The moon goes by many names. August saw the full sturgeon moon while in March sky-gazers may have witnessed the blood moon, which occurs when the satellite appears to turn red during a lunar eclipse. You may have also heard of a blue moon, the second full moon to happen in one month.
And then there is the black moon, occurring this weekend, which is rare — and invisible.
This phenomenon will occur Friday night into the early hours of Saturday. The moon will be closest to the sun at 2:06 a.m. ET Saturday, according to EarthSky.
[url=https://skyiwredshjnhjgeleladu7m7mgpuxgsnfxzhncwtvmhr7l5bniutayd0.net]skyiwredshjnhjgeleladu7m7mgpuxgsnfxzhncwtvmhr7l5bniutayd onion[/url]
What is a black moon?
Like a blue moon, a black moon isn’t an official term, but it refers to the second new moon in a month. It happens once every 29 months.
A new moon occurs when only its far side is illuminated by the sun, making it invisible from Earth. It marks the beginning of the lunar cycle.
“A black moon (or new moon) is when the moon is basically in between the Earth and the sun, not to make an eclipse, but where we don’t see the moon,” said Noah Petro, chief of NASA’s Planetary, Geology, Geophysics and Geochemistry Laboratory at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
https://blacksprut2rprrt3aoigwh7zftiprzqyqynzz2eiimykw7wkpyad.com
skyiwredshjnhjgeleladu7m7mgpuxgsnfxzhncwtvmhr7l5bniutayd.onion
What makes it different from a solar eclipse is the placement of the moon. In a solar eclipse, the moon passes in front of the sun, blocking some or all the sunlight and casting a shadow on Earth. But a new moon (and black moon) passes near the sun.
The term black moon can also refer to a month in which there are no new moons. This typically happens in February because the lunar cycle follows a pattern of 29.5 days, according to Petro. February usually has 28 days, except on leap years when it has 29 days.
Stargazers may have quite a view
Since the black moon will be invisible, moon watchers won’t have much to see.
But stargazers will have plenty.
“A new moon or the black moon is great for astronomers when it’s clear,” Petro said, “because you can go outside and have basically no light contamination from the moon.”
This is the best time of year to see planets, according to EarthSky, so after sunset or just before sunrise, you might be able to spot some celestial bodies, such as Venus, Mars and Saturn.
If you have binoculars or a telescope, you can also keep an eye out for the dumbbell nebula, the colorful, glowing remnants of an old star 1,200 light-years from Earth in the Vulpecula constellation. The nebula appears during the first half of the night.
Мы работаем с вниманием к деталям повседневности: как человек засыпает на фоне вечернего света, сколько воды переносит малыми глотками, как реагирует на цифровые уведомления, есть ли привычные «включатели» тяги и как на организм влияет шумное окружение. Врач и куратор переводят этот жизненный контекст в ясные, измеримые ориентиры: время до сна, число пробуждений, вариабельность пульса к сумеркам, объём воды, аппетит, переносимость тёплой мягкой пищи. Решения принимаются адресно и последовательно, чтобы сохранять ясность днём и избегать ненужной фармаконагрузки.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kaliningrad15.ru/]вывод наркологическая клиника[/url]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Расширить кругозор по теме – http://gasreturn.ru/ordshp/21
В крупных и динамичных районах Ставрополя дорога сама по себе становится стрессором: непривычные запахи, чужие люди, ожидание в коридоре — всё это усиливает тремор, реактивность пульса и «ночной разгон» мыслей. Именно поэтому «СтаврМедЦентр» предлагает аккуратный выбор: если объективные риски низкие, мы начинаем дома или амбулаторно и переносим часть «тяжёлых» решений в первый вечер. Там проще включить светогигиену, отрегулировать шум, наладить воду и положить рядом тёплую лёгкую пищу. Когда среда управляемая, меньше соблазн «усилить» схему лишними препаратами, и организм быстрее выходит на коридоры безопасности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-stavropol15.ru/]запой наркологическая клиника[/url]
Поэтапная структура терапии делает лечение контролируемым и прогнозируемым, минимизируя риски возникновения осложнений и повторных обострений зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/narkologicheskie-dispansery-sankt-peterburga/
Реабилитационные мероприятия в клинике направлены на устранение соматических последствий зависимости, нормализацию когнитивных функций и восстановление социальной адаптации. Для этого используются современные методики физиотерапии, диетологической коррекции и психологического сопровождения, позволяющие закрепить достигнутые результаты лечения.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-spb16.ru/narkolog-sankt-peterburg/
framework concepts portal – Clear organization and explanation make business concepts easy to follow.
Explore xeviro core – Information is presented logically, and the site feels professional.
professional service portal – Straightforward styling keeps focus on the services provided.
Снижается тремор и тошнота, выравниваются вегетативные реакции, возвращается способность спокойно уснуть. Вместо «качелей» настроения и попыток самолечения появляется ощущение контроля: понятно, что делаем сейчас и чего ждём дальше.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru/vyvesti-iz-zapoya-v-odincovo/
Инфузионная терапия подбирается под человека, а не под «среднюю» ситуацию. Базовый каркас обычно включает растворы для регидратации и коррекции электролитов, витамины группы B и магний для поддержки нервной системы. По показаниям добавляются гепатопротекторы и антиоксидантные компоненты — это помогает печени и снижает оксидативный стресс. Если есть выраженная тошнота, подключаем противорвотные; при тревоге и нарушении сна — мягкие анксиолитики и седативные препараты, которые не «вырубают», а выравнивают ритмы и сохраняют контакт для мониторинга. Мы избегаем агрессивных «миксов», потому что избыточная седация может скрыть опасные симптомы и усложнить оценку состояния. Эффективность оцениваем не только по субъективному облегчению, но и по объективным метрикам: пульс, давление, сатурация, динамика тремора, аппетит, качество сна. Как только показатели стабилизируются, фарм-нагрузка снижается, а ведущую роль берет режим — питание, гидратация, спокойный вечерний ритуал, короткие бытовые активности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Разобраться лучше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika-v-krasnogorske/
Сначала — сбор короткого анамнеза и проверка лекарственных взаимодействий, затем — старт инфузии с контролем темпа. Параллельно купируются тошнота, тремор, тахикардия, корректируется сон. Каждые 15–20 минут специалист оценивает динамику и при необходимости меняет схему. В завершение вы получаете письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnogorske
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Выяснить больше – срочный вывод из запоя
Выезд на дом удобен, но не всегда безопасен. Если запой длится больше трёх–пяти суток, присутствует повторная рвота, выраженная слабость, спутанность сознания, судорожная готовность или резкие «качели» давления и пульса, лучше не тянуть и ехать в стационар. Для пациентов старшего возраста и при тяжелой соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические заболевания печени/почек) круглосуточный мониторинг уменьшает риск осложнений и позволяет гибко расширять схему лечения. В стационаре доступна приборная диагностика, тщательный контроль жизненных показателей и быстрая коррекция терапии, если клиническая картина меняется. Мы организуем медицинскую транспортировку, встречу на входе, расширенный осмотр и запуск персонального протокола без задержек. Семья при этом остаётся в информационном контуре: врач объясняет смысл каждого шага и ожидаемый эффект, чтобы решения были осознанными, а не продиктованными паникой или усталостью.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/kruglosutochno-vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-krasnogorske
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – бесплатные порно видео
Сначала — короткое интервью по телефону: адрес в Одинцово, длительность запоя, препараты, хронические заболевания, аллергии. Это экономит 15–20 минут на месте и помогает заранее спланировать безопасные дозы. По прибытии — осмотр, запуск инфузий и параллельная симптоматическая терапия: противорвотные при тошноте, анксиолитики при тревоге, аккуратная седация к ночи, если есть бессонница. Мы не «усыпляем» пациента — поддерживаем контакт для информативного мониторинга. На протяжении процедуры фиксируем динамику, регулируем скорость капельниц, выстраиваем щадящую гидратацию и лёгкое питание. Если картина меняется, быстро перестраиваем план. На выходе — письменные рекомендации и маршрут продолжения (амбулаторные визиты, дневной стационар или полноценное отделение). Такой алгоритм убирает случайность результата: эффект держится не на удаче, а на чётких действиях команды и дисциплине первых суток.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo10.ru
Критичные случаи, когда вызов нарколога через «МедТрезвие Долгопрудный» оправдан и своевременен:
Углубиться в тему – http://narkolog-na-dom-dolgoprudnij10.ru/
Врач приезжает с одноразовыми системами и препаратами, проводит экспресс-диагностику, стартует инфузии и каждые 15–20 минут оценивает динамику, корректируя темп и состав. По завершении — памятка по режиму, гигиене сна, питанию и запретам на 24–72 часа, а также контакты для связи ночью.
Подробнее – нарколог вывод из запоя
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk10.ru/
В Одинцово доступен гибкий маршрут: выездная бригада 24/7 и стационар. Домашний формат хорош при умеренной симптоматике и сохранённом контакте — он позволяет избежать перевозок и сохранить конфиденциальность. Стационар предпочтителен при длительном эпизоде, повторной рвоте, выраженной слабости, нестабильном давлении/пульсе, спутанности сознания, судорожной готовности, а также у пациентов старшего возраста и при тяжёлой соматике (ИБС, гипертония, диабет, хронические болезни печени/почек). Мы оцениваем не один признак, а совокупность факторов и динамику, чтобы не «пересидеть» дома там, где нужен приборный мониторинг. В обоих вариантах сохраняется наш принцип: индивидуализация схемы, осторожная седация, прицельная работа со сном, прозрачные объяснения назначений — и всё это с опорой на объективные показатели, а не ощущения «полегчало/ухудшилось».
Разобраться лучше – http://www.domen.ru
Этот информационный набор привлекает внимание множеством мелочей и странных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем взгляды, которые редко бывают полезны, но могут слегка разнообразить ваше знакомство с темой.
Вот – взрослые игры
Круглосуточное наблюдение, регулярные замеры, быстрые корректировки, спокойная среда и структурированный режим. Это снижает риски ночных ухудшений и помогает мягко «собрать» сон без агрессивных седативных решений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя на дому одинцово
Выездная бригада «МедОпоры» дежурит 24/7 и покрывает весь Красногорск и близлежащие районы. После короткого звонка дежурный уточняет длительность запоя, сопутствующие болезни, принимаемые препараты и аллергии — это экономит время на месте и помогает заранее предусмотреть риски. Врач приезжает с комплектом одноразовых систем, растворами и медикаментами, проводит экспресс-диагностику: измерение давления, пульса, сатурации, температуры, оценка неврологического статуса, степени обезвоживания и тревожности. По этим данным формируется индивидуальная схема инфузий и симптоматической поддержки. Наша задача — не просто «поставить капельницу», а безопасно развернуть план стабилизации, где дозировки и темп меняются по реакции организма. Если выявляются признаки осложнений или дома нет условий для безопасного наблюдения, сразу предлагаем перевод в профильный стационар, чтобы не терять драгоценные часы. Семья получает понятные роли и инструкции, а врач остаётся на связи для уточнений по режиму ближайшей ночи.
Получить больше информации – врач вывод из запоя
Круглосуточное наблюдение, регулярные замеры, быстрые корректировки, спокойная среда и структурированный режим. Это снижает риски ночных ухудшений и помогает мягко «собрать» сон без агрессивных седативных решений.
Выяснить больше – anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-odincovo
Подавляющее число абонентов в Новосибирской области постоянно жалуются на:
– нестабильный сигнал;
– ограниченную скорость в часы пик;
– сложности с настройкой оборудования.
Выбор дешёвого провайдера без проверки часто приводят к:
– разочарованию;
– ухудшению качества связи;
– переплатам за ненужные услуги.
Только надёжный провайдер обеспечивает:
– бесперебойный сигнал;
– прозрачные тарифы без скрытых платежей;
– гарантию качества.
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предоставляют:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• бесплатный монтаж оборудования;
• бонусы для новых абонентов.
• Комплексный анализ доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Анализ инфраструктуры по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку оборудования
• Индивидуальную помощь менеджера
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]интернет сибсети тарифы новосибирск[/url]
сибирские сети домашний интернет тарифы московская область – [url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]https://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru[/url]
[url=http://globaltradeimportexport.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://911proof.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.educ-ua7.ru/www.rudik-diplom13.ru/www.rudik-diplom14.ru]Интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в Новосибирске[/url] cbd6_6d
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предоставляют:
• высокоскоростной интернет до 500 Мбит/с;
• поддержки 24/7;
• бонусы для новых абонентов.
• Комплексный анализ доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального тарифа под ваши задачи
• Проверку технической доступности по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж роутера
• Индивидуальную помощь менеджера
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]интернет сибирские сети тарифы новосибирск[/url]
сибирские сети тарифы домашний интернет и телевидение новосибирск – [url=http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /]http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /[/url]
[url=http://americanlithoinc.biz/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]http://hardtargets.net/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=https://grandbavarchi.com.au/product/chicken-65/#comment-26251]Домашний интернет и ТВ от «СибСети» в Новосибирске[/url] 8b64918
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持全球加速观看。
爱一帆下载海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台采用机器学习个性化推荐,支持全球加速观看。
爱一凡海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频官方认证平台,支持全球加速观看。
海外华人必备的iyf官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
«Field Fit» предоставляет:
• футболки из быстросохнущей ткани;
• товары для взрослых, детей и женщин;
• Определение оптимального набора под ваш клуб и бюджет;
• Анализ наличия размеров.
[url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]футбольная атрибутика в москве[/url]
магазин футбольной формы в москве – [url=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru]http://www.futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.com.om/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/]http://www.google.co.zw/url?q=https://futbolnaya-forma-fieldfit.ru/[/url]
[url=http://druk3d.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=135882]Спортивная экипировка и подарки для фанатов от «Field Fit» в вашем городе[/url] cbd3_ac
Натяжные потолки в Архангельске — быстро,качественно,с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональный монтаж в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем практичный вариант натяжных потолков с учётом особенностей помещения;
Выполняем работы любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор матовых полотен.
Рассчитаем стоимость — свяжитесь с нами!
Потолки под ключ в ванной — любая фактура. В Архангельске — с консультацией специалиста-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки на кухню в архангельске[/url]
натяжные потолки глянцевые – [url=https://29-potolok.ru]http://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.dz/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/]https://images.google.ie/url?sa=t&url=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.pelsh.forum24.ru/www.arus-diplom24.ru/www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya.ru/pinup5007.ru]Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] be408cb
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/cs/register-person?ref=OMM3XK51
Real Money Casino Australia Feel Like A True High Roller
Best Pokies Real Money Australia Real Thrill Of Multi-Million Hits
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предоставляют:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• Точную оценку покрытия сети в вашем доме
• Определение оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи
• Анализ технической доступности по вашему адресу
• Профессиональную установку ТВ приставки
• Прозрачные условия на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]сибирские сети тарифы на интернет и телевидение новосибирск[/url]
сибирские сети установка интернета – [url=http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]http://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru /[/url]
[url=https://images.google.com.tw/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]https://cse.google.com.lb/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=http://jkasiege.net/viewtopic.php?t=812476]Интернет и телевидение от «СибСети» в Новосибирске[/url] 2f9b5c5
«СибСети» в Новосибирске предлагают:
• интерактивное ТВ;
• Точную оценку доступных технологий в вашем доме
• Подбор оптимального пакета услуг под ваши задачи
• Анализ технической доступности по вашему адресу
• Грамотный монтаж ТВ приставки
• отсутствие скрытых платежей на весь срок обслуживания
[url=internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]сибсети домашний интернет тв[/url]
подключить домашний интернет в новосибирске сибсети – [url=http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru]http://www.internet-sibirskie-seti.ru[/url]
[url=http://www.google.com.ng/url?q=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/]https://clients1.google.com.vc/url?sa=t&url=https://internet-sibirskie-seti.ru/[/url]
[url=http://www2.saganet.ne.jp/cgi-bin/hatto/board/wwwboard.pl/www.iskusstvennaya-kozha-dlya-mebeli-kupit.ru/www.sportbets31.ru/www.samokleyushchayasya-plenka-1.ru/melbet5013.ru]Интернет и цифровое ТВ от «СибСети» в вашем доме[/url] 8b64918
Натяжные потолки в Архангельске — качественно, быстро и с гарантией.
Осуществляем проффессиональную установку за 1 день в ванную, на кухню, в комнату, в коридор;
Подберем идеальное решение натяжных потолков с учётом особенностей помещения;
Выполняем работы любой сложности, предлагаем большой выбор сатиновых полотен.
Приедем на замер — напишите!
Натяжные потолки в ванной — любая сложность. в Архангельском регионе — с консультацией специалиста-
[url=https://29-potolok.ru/]натяжные потолки матовые в архангельске высота[/url]
натяжные потолки двухуровневые в архангельске высота – [url=http://www.29-potolok.ru/]http://www.29-potolok.ru[/url]
[url=https://www.google.com.fj/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/]https://clients1.google.sm/url?q=https://29-potolok.ru/[/url]
[url=http://fejari.com/product/sophia-ring-bcg]Профессиональный монтаж натяжных потолков в Архангельске: быстро, качественно, с гарантией[/url] 8cbd1_d
Cộng đồng đang xôn xao về nhà cái CM88. Thấy hot quá nên vào xem sao thì thấy dịch vụ bên này quá ổn.
Anh em nào chưa biết thì nên thử nhé.
quality picks hub – Nice assortment, browsing feels fast and secure.
u888 – thiên đường giải trí số 1 Việt
Nam, cơ hội đổi đời năm 2026 trong tầm tay
Take a look at my web page … thể thao u888
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/id/register?ref=UM6SMJM3
huarenus官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
Chia sẻ cho cả nhà sân chơi xanh chín số 1 hiện nay là thương hiệu F8bet.
F8bet đang là top 1 thị trường. Kèo cược đa dạng không thiếu món gì.
Bác nào chưa có tài khoản thì đăng ký ngay nhé.
цвет в дизайне интерьера создание дизайна интерьера
Проблемы с зубами? стоматологический центр профилактика, лечение, протезирование и эстетическая стоматология. Забота о здоровье зубов с применением передовых методик.
Охраны труда для бизнеса центр охраны труда аудит системы безопасности, обучение персонала, разработка локальных актов и внедрение стандартов. Помогаем минимизировать риски и избежать штрафов.
Professional сonstruction Moraira: architecture, engineering systems, and finishing. We work with local regulations and regional specifics in mind. We handle permitting and material procurement so you can enjoy the creative process without the stress of management.
Нужен фулфилмент? фулфилмент для маркетплейсов — хранение, сборка заказов, возвраты и учет остатков. Работаем по стандартам площадок и соблюдаем сроки поставок.
Запчасти для сельхозтехники https://selkhozdom.ru и спецтехники МТЗ, МАЗ, Амкодор — оригинальные и аналоговые детали в наличии. Двигатели, трансмиссия, гидравлика, ходовая часть с быстрой доставкой и гарантией качества.
Получение медицинской https://gira-spravki2.ru справки с доставкой после официального оформления. Комфортная запись, минимальные сроки и законная выдача документа.
Орби казино https://orby-casino.com/ онлайн-платформа с широким выбором слотов, настольных игр и бонусных предложений. Узнайте об акциях, турнирах и возможностях для комфортного игрового досуга.
Онлайн казино Орби orby-casino.net большой выбор слотов, бонусы для новых и постоянных игроков, регулярные турниры с призами.
24小時即時更新nba賽程比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
help me write my paper top casino
Лучшие https://casinonodeposit.ru — бесплатные бонусы для старта, подробные обзоры и сравнение условий различных платформ.
马赛客场硬刚布雷斯特!2026法甲20:45生死战,姆巴佩旧将能否带队翻盘?法国足球最新赛事比分火热预测中!
迪丽热巴陈飞宇《慕胥辞》2026古装爱情巨制,海外华人免费高清热播,虐心又甜蜜,全球加速无缓冲播放,2026古装天花板。
辛芷蕾林雨申《女神蒙上眼》2026都市悬疑职场大戏,海外华人必备高清陆剧,职场暗战烧脑刺激,全球加速实时更新无广告追剧首选。
2026 football news: Forest’s 3-0 masterclass in Europa League sets tone – latest match results show Premier League clubs dominating Europe!
Looking for a yacht? Cyprus luxury boat tours for unforgettable sea adventures. Charter luxury yachts, catamarans, or motorboats with or without crew. Explore crystal-clear waters, secluded bays, and iconic coastal locations in first-class comfort onboard.
купить кабель метрами проводка купить
Нужны столбики? столбики ограждения с лентой купить столбики для складов, парковок и общественных пространств. Прочные материалы, устойчивое основание и удобство перемещения обеспечивают безопасность и порядок.
Selected articles: https://hack.allmende.io/s/fsdmsejv9
мобильные стойки ограждения мобильная стойка
дешевые свадебные платья купить каталог свадебных платьев с ценами
сео продвижение по трафику [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-trafiku6.ru/]сео продвижение по трафику[/url] .
зробити ремонт у 2 квартирі послуги ремонту квартир
оптимизация и seo продвижение сайтов москва [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve11.ru/]оптимизация и seo продвижение сайтов москва[/url] .
маркетинговые стратегии статьи [url=https://seo-blog15.ru/]seo-blog15.ru[/url] .
блог о маркетинге [url=https://seo-blog14.ru/]блог о маркетинге[/url] .
mellstroy casino сайт [url=https://t.me/mellstroy_ggame/]mellstroy casino сайт[/url] .
seo partner [url=https://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve11.ru/]prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve11.ru[/url] .